paralysis treatment at home

These Might be of Interest

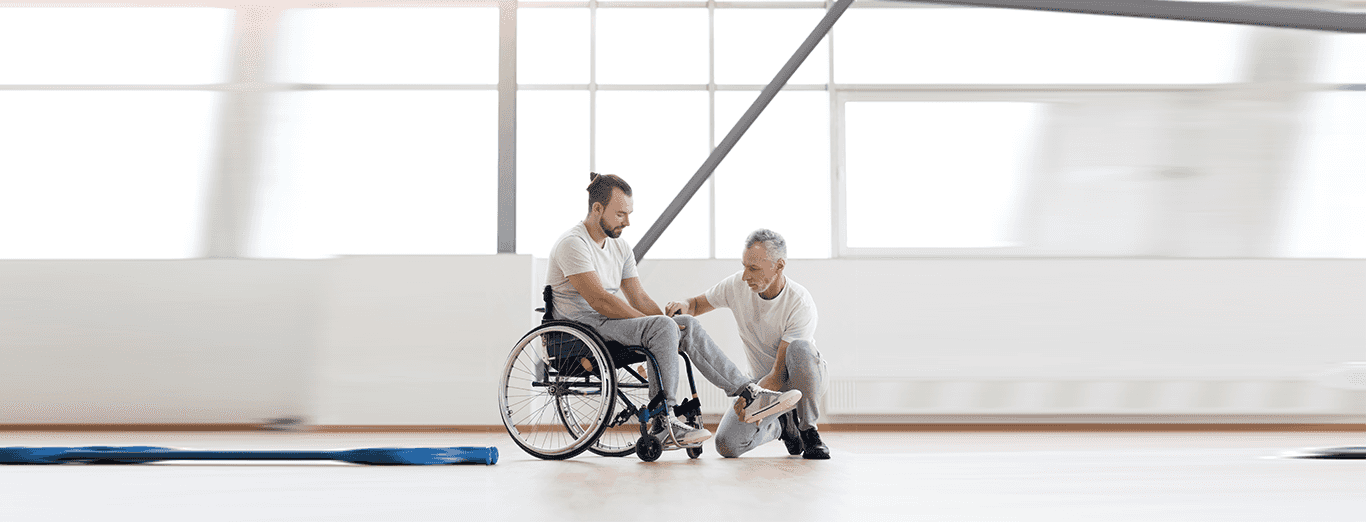
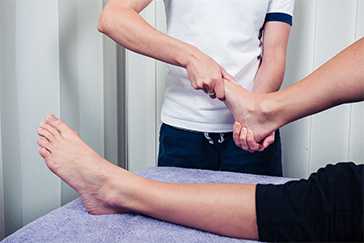
paralysis treatment at home
Paralysis treatment focuses on improving functionality and enhancing quality of life through various approaches. Physical therapy involves exercises and stretches to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Occupational therapy assists individuals in performing daily activities and adapting their surroundings with the help of assistive devices. Medications are used to manage symptoms like pain and muscle spasticity. In certain cases, surgery may be required to address underlying conditions or repair nerve damage. Comprehensive rehabilitation programs often integrate physical, occupational, and, when needed, speech therapy for holistic care.
types of paralysis?
Here are the definitions of different types of paralysis:
- Monoplegia: Paralysis that affects a single limb, either an arm or a leg, often caused by conditions such as stroke, trauma, or neurological disorders.
- Hemiplegia: Paralysis on one side of the body, either the left or the right, typically resulting from a stroke or brain injury that impacts one hemisphere of the brain.
- Paraplegia: Paralysis of the lower half of the body, including both legs and occasionally part of the trunk. It is commonly caused by spinal cord injuries or neurological conditions affecting the lower spinal cord.
- Quadriplegia: Paralysis of all four limbs—both arms and legs—usually caused by spinal cord injuries or conditions affecting the cervical spine, leading to loss of function in all limbs.
causes of paralysis
The most common cause of paralysis is a stroke, which can damage the brain and disrupt its connection to the spinal cord.
Here are the primary causes of paralysis:
- Spinal Cord Injury: Damage to the spinal cord can lead to loss of sensation, function, or movement below the injury site. Depending on the injury’s severity and location, it can cause paralysis or weakness.
- Multiple Sclerosis: This chronic autoimmune disorder affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, causing symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, numbness, and coordination issues.
- Cerebral Palsy: A group of neurological disorders caused by damage to the developing brain, typically before or during birth. It affects movement, posture, and muscle coordination, leading to lifelong motor skill challenges.
- Post-Polio Syndrome: A condition that emerges years after recovering from polio, characterized by new muscle weakness, fatigue, and pain.
- Neurofibromatosis: A genetic disorder that leads to the growth of tumors on nerve tissue. Symptoms vary based on tumor type and location and may include skin abnormalities, vision problems, and nerve impairments.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Brain damage caused by an external force, such as a blow or jolt to the head. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, and emotional impairments, depending on the injury’s severity and location.
- Birth Defects: Structural or functional abnormalities present at birth, often affecting the brain, spine, heart, or limbs. These defects can result from genetic factors, environmental exposures, or a combination of both.
symptoms of paralysis
Our ability to move is governed by the coordination between sensory nerves and the central nervous system. Any disruption in the transmission of nerve signals along the pathway from the brain to the muscles can hinder muscle control, leading to muscle weakness and a loss of coordination. Over time, this muscle weakness may develop into paralysis, with symptoms potentially manifesting in any part of the body.
- Loss of consciousness: A sudden inability to remain awake or aware, often indicating severe brain or neurological damage.
- Clumsiness and numbness: Difficulty coordinating movements and a loss of sensation in certain body parts, often signaling nerve or brain issues.
- A severe headache: Intense pain in the head, which may be a warning sign of stroke or brain injury.
- Difficulty breathing: An inability to breathe properly due to impaired muscles or nerve function, sometimes requiring immediate medical attention.
- Drooling: Inability to control facial muscles, causing saliva to escape uncontrollably, often linked to neurological conditions.
- Cognitive difficulties, difficulty writing or speaking: Challenges with thinking, memory, or communication, indicative of brain damage or dysfunction.
- Changes in mood or behavior: Unusual emotional reactions or altered personality, often resulting from brain injury or neurological disorders.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control: Inability to manage urination or defecation due to nerve or muscle damage affecting bodily functions.
- Loss or changes in vision and/or hearing: Sudden visual or auditory impairments, signaling possible nerve or brain damage.
- Nausea with or without vomiting: A sensation of sickness in the stomach, sometimes associated with neurological or vestibular system problems.
management of paralysis
Managing and treating paralysis involves a holistic approach focused on enhancing function, mobility, and overall quality of life. Key strategies include:
- Physical Therapy: Aims to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and increase mobility through specific exercises and stretches.
- Occupational Therapy: Supports individuals in adapting to daily activities by training them to use assistive devices and make necessary home modifications to maintain independence.
- Medications: Helps control symptoms such as pain and muscle spasticity using muscle relaxants, pain relievers, or anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Assistive Devices: Incorporates tools like wheelchairs, braces, and prosthetics to improve mobility and facilitate daily living.
- Surgical Interventions: Involves procedures to address underlying conditions or repair nerve damage, such as spinal surgeries or decompression techniques.
physiotherapy treatment for paralysis
Physiotherapy treatment for paralysis is customized to each individual’s condition, based on a thorough neurological assessment. Following the evaluation, goals and expectations are outlined. Treatment often includes muscle strengthening exercises, stretches to preserve joint mobility, core stability training, dynamic balance exercises, and re-education of walking patterns. Additional approaches may involve sensory stimulation, functional electrical stimulation, hydrotherapy, and the use of gym equipment. Educating caregivers and providing walking aids or other supportive equipment are also essential components of the therapy.
prevention for paralysis
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Consuming a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol can support nerve and muscle health.
- Prevent Injuries: Using seatbelts, protective sports gear, and ensuring home safety measures can reduce the risk of spinal cord injuries or traumatic brain damage.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Controlling conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol can lower the risk of stroke and nerve-related complications.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine medical screenings can help detect and manage potential risk factors like high blood pressure or nerve disorders early.
- Vaccinations: Staying updated on vaccines, such as the polio vaccine, can prevent infections that might cause paralysis.
- Prevent Infections: Practicing good hygiene and avoiding exposure to harmful bacteria or viruses can protect the nervous system from infections like meningitis.
- Stress Management: Adopting relaxation techniques and managing chronic stress helps maintain overall neurological health.
- Prompt Treatment of Symptoms: Immediate medical attention for symptoms like sudden weakness or numbness can prevent conditions from worsening.
- Healthy Weight Management: Keeping a healthy weight reduces strain on the spine and joints, lowering the likelihood of nerve compression or spinal damage.
how can portea help you?
Portea supports your recovery and enhances your quality of life with expert at-home diagnostics, personalized physiotherapy, targeted pain management, customized exercise programs, and preventive strategies. Our holistic healthcare services provide convenient, accurate, and tailored care, empowering you to take charge of your health journey.
portea’s other services
With Portea, you’re not just getting the best paralysis physiotherapy Treatment At Home with a physiotherapist for paralysis; you’re gaining a partner in your journey to recovery and well-being. We also offer a range of superior healthcare services, including doctor consultations, medical equipment, nursing care, and dedicated trained attendants. Rely on us for top-tier healthcare solutions tailored to your requirements.
MEET OUR PHYSIOTHERAPISTS FOR PARALYSIS
Dr.L Swarna Harini-MPT/BPT – 6 years Experience
Dr. Hari Prasad M – MPT – 4 years Experience.
Dr.Neha Suhas Kulkarni – MPT- 4.5 years Experiences
More
faq’s
How common is paralysis?
Paralysis is a relatively common condition, with millions of people affected globally. It can result from various causes, such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, and neurological disorders. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 250,000 to 500,000 people suffer from spinal cord injuries each year, while strokes remain one of the leading causes of paralysis. The prevalence of paralysis varies depending on the region, with certain conditions, like cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis, being more common in specific populations.
Can I recover from paralysis?
Recovery from paralysis depends largely on the cause, severity, and timeliness of medical intervention. While some individuals can experience partial or even full recovery, especially if the paralysis is caused by treatable conditions like a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mild injury, others may face long-term or permanent effects. Rehabilitation, including physical and occupational therapy, plays a crucial role in maximizing recovery by helping individuals regain muscle strength, improve mobility, and adapt to daily life with assistive devices or adaptive techniques.
What is the prognosis (outlook) for people who have paralysis?
The prognosis for individuals with paralysis depends on the location and extent of nerve damage, as well as the underlying cause. In some cases, paralysis can improve with rehabilitation, and individuals may regain a significant degree of function. However, for others, especially those with complete spinal cord injuries or severe brain damage, the outlook may involve lifelong dependency on support and adaptive equipment. With proper medical care, therapy, and assistive devices, many individuals with paralysis can lead fulfilling lives, though the degree of recovery varies greatly among individuals.
How does paralysis affect the body?
Paralysis disrupts the communication between the brain and muscles, resulting in the loss of movement and sensation in the affected body parts. The impact can range from partial weakness and reduced mobility to complete immobility in severe cases. In addition to motor function loss, paralysis can affect other bodily systems, such as bladder and bowel control, respiration, and circulation, depending on the severity and location of the paralysis. Paralysis often requires extensive rehabilitation and adaptive strategies to manage daily activities and maintain overall health.
What is the best treatment for paralysis
The best treatment for paralysis is a multidisciplinary approach that focuses on improving function, managing symptoms, and enhancing the quality of life. This typically includes physical therapy to strengthen muscles and improve mobility, occupational therapy to assist with daily activities, medications to control pain, muscle spasticity, or inflammation, and assistive devices like wheelchairs, braces, or prosthetics to aid movement. In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address underlying issues, such as spinal cord decompression or nerve repair. Early intervention, ongoing rehabilitation, and a supportive care team are essential for optimizing recovery and improving long-term outcomes.
References
Doctor Consultation
Nursing
Physiotherapy
Trained Attendant
Elder Care
Mother & Baby Care
Lab Tests
Medical Equipment
Speciality Pharma
Critical Care