physiotherapy treatment for bursitis knee

These Might be of Interest

what is knee bursitis?
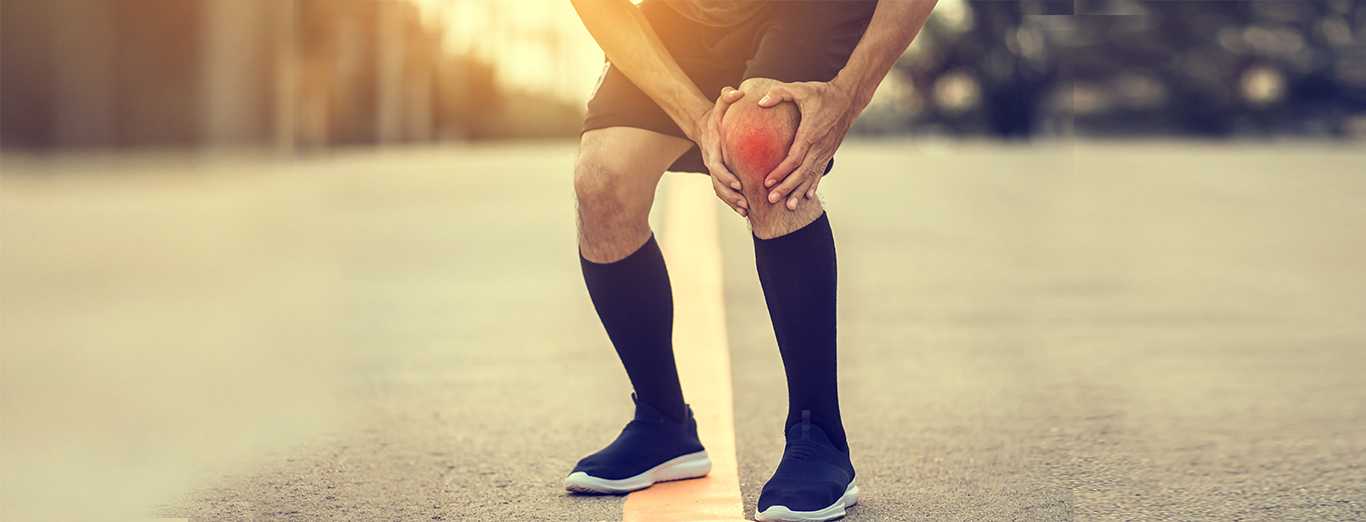
Knee bursitis, or prepatellar bursitis, involves inflammation of the bursa—a small fluid-filled sac near the knee joint. These sacs cushion and protect the knee bones and tendons from friction. Primarily affecting the kneecap or the inner side of the knee, knee bursitis can cause discomfort. Proper care is crucial to maintain the health and function of the knee joint and its surrounding structures.
types of knee bursitis:
A bursa is a fluid-filled sac found between the skin and tendon, as well as between the tendon and bone. Its primary role is to reduce friction between moving structures. There are several types of bursae around the kneecap, and inflammation of one of these can lead to bursitis. The different types of knee bursitis include:
- Prepatellar Bursitis: Involves inflammation of the bursa over the kneecap, causing pain and swelling at the front of the knee.
- Infrapatellar Bursitis: Affects the bursa beneath the kneecap, leading to discomfort and swelling, often due to repetitive stress or injury.
- Superficial Infrapatellar Bursitis: Involves inflammation of the bursa just below the kneecap, usually from trauma or friction, resulting in localized pain and swelling.
- Deep Infrapatellar Bursitis: Affects the deeper bursa beneath the kneecap, often caused by excessive kneeling or overuse, leading to pain and swelling.
- Suprapatellar Bursitis: Involves inflammation of the bursa above the kneecap, commonly associated with conditions like arthritis, causing pain and discomfort in the upper part of the knee.
causes of knee bursitis
There are various causes of knee bursitis, with some common ones including:
- Frequent kneeling or prolonged pressure on hard surfaces
- Overuse or strenuous activities such as running, hiking, or climbing
- Trauma to the knee
- Bacterial infection of the bursa
- Other health conditions like osteoarthritis, gout, and rheumatoid arthritis
symptoms of knee bursitis
The symptoms of knee bursitis can vary depending on the affected bursa. They typically develop gradually and may worsen over time or following an injury. Common symptoms include swelling of varying degrees, warmth, tenderness, and redness around the inflamed bursa. Individuals with knee bursitis often experience pain while walking, stiffness when kneeling, and restricted knee mobility.
knee bursitis diagnosis
The primary diagnosis of knee bursitis involves a physical examination of the knee, including comparing the affected knee with the unaffected one, applying slight pressure to assess warmth and tenderness, and evaluating pain, site, and knee mobility.
In addition to the physical exam, doctors may recommend imaging tests for a more accurate diagnosis. These tests can include X-rays, ultrasound, MRI scans, and aspiration in cases of gout.
home treatment for knee bursitis
For knee bursitis relief, several home remedies can be effective, including the RICE method: resting the knee, keeping it elevated, applying an ice pack, and wrapping the knee with an elastic bandage to reduce swelling. Additional remedies for knee bursitis relief include:
- Performing knee bursitis exercises as recommended by a physiotherapist
- Maintaining a healthy weight and staying in good physical condition
- Warming up properly before engaging in sports or exercise
- Avoiding prolonged kneeling and taking breaks as needed
knee bursitis treatment
The treatment for knee bursitis varies depending on whether the condition is septic or aseptic.
Aseptic Knee Bursitis: Can often be managed at home with remedies, medications, injections, and physical therapy.
- Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics are commonly prescribed for pain and inflammation relief.
- injections: Cortisone injections may be administered if medications do not provide sufficient relief.
- Physical Therapy: Also referred to as physiotherapy, involves exercises to strengthen and stretch the knee, improve mobility, and reduce pain and stiffness.
Septic Knee Bursitis: Requires more advanced medical treatment, which may include:
- Aspiration: Involves extracting fluid from the infected bursa using a needle, which can be analyzed for diagnosis and treatment.
- Surgery: Considered only in severe cases or when conservative treatments fail. The procedure involves removing the affected bursa to alleviate symptoms.
how can we help?
Knee bursitis causes pain with even walking and as such knee bursitis home treatment is best recommended for such people. Portea with its highly trained healthcare professionals can bring an entire clinic to your doorstep as such. If you need knee bursitis knee physical therapy just get in touch with us and allow us to rapidly nurse you back to good health.
With Portea, you’re not just getting physiotherapy at home for Knee bursitis; you’re gaining a partner in your journey to recovery and well-being. We also offer a range of superior healthcare services, including doctor consultations, medical equipment, nursing home care, and dedicated caretakers. Rely on us for top-tier healthcare solutions tailored to your requirements.
MEET OUR RENOWNED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS FOR KNEE BURSITIS
- Dr. A Franklin Rajkumar – BPT – 10 years Experience
- Dr.L Swarna Harini-MPT/BPT – 6 years Experience
- Dr. Ramya Deepika.C.C -MPT -7 years Experience.
faq’s
What Are the Best Exercises for Knee Bursitis?
- Lie on your back with the affected knee straight and the healthy knee bent.
- Gently bend your affected knee by sliding your heel towards your buttock until you feel a mild stretch.
- Hold the stretch for about 6 seconds, then slowly straighten your knee.
- Repeat this exercise 8-12 times.
What Should You Avoid if You Have Knee Bursitis?
- Take regular breaks if you need to kneel for extended periods; stretch your legs and rest your knees frequently.
- Avoid excessive squatting, as repetitive bending of the knees puts additional strain on the knee joints.
What Are the Three Main Signs of Bursitis?
Common symptoms of bursitis include pain, swelling, and tenderness around the affected joint. Bursitis can be treated with rest and anti-inflammatory medications.
What are Essential Physical Therapy Tips for Knee Bursitis Recovery
Essential Physical Therapy Tips for Knee Bursitis Recovery
- Follow a Personalized Exercise Program: Work with your physical therapist to develop a tailored exercise routine that targets strength and flexibility without aggravating your condition.
- Perform Stretching Exercises: Incorporate gentle stretches to improve flexibility and reduce stiffness. Focus on exercises that gently stretch the muscles around the knee.
- Strengthen Supporting Muscles: Strengthen the muscles around the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, to provide better support and reduce stress on the bursa.
- Use Proper Techniques: Ensure you use correct techniques for exercises and daily activities to prevent additional strain on the knee.
- Apply Ice and Heat: Use ice packs to reduce inflammation and heat packs to relax tight muscles, as recommended by your therapist.
How can I prevent the recurrence of knee bursitis?
Preventing the recurrence of knee bursitis involves several key steps:
- Identify and Address Risk Factors: Recognize activities that may contribute to knee bursitis, such as repetitive movements, poor biomechanics, or improper equipment. Work on correcting these issues to reduce risk.
- Follow Proper Warm-Up and Stretching Techniques: Learn and apply correct warm-up and stretching techniques from your physiotherapist to avoid straining your knee.
- Use Appropriate Footwear and Protective Gear: Ensure you wear suitable footwear and use proper protective gear and equipment for your activities.
- Maintain a Consistent Exercise Routine: Adhere to a regular exercise regimen to strengthen and support your knee, and keep up with your physiotherapy exercises.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Continue with follow-up appointments and assessments to ensure ongoing knee health and to make necessary adjustments to your prevention strategy.
References
Doctor Consultation
Nursing
Physiotherapy
Trained Attendant
Elder Care
Mother & Baby Care
Lab Tests
Medical Equipment
Speciality Pharma
Critical Care